The United States is the world's largest country for cell therapy research and development, with 374 gene and cell therapy (CGT) clinical trials registered in the INFORMA drug database, and the United States is far ahead with 120 clinical trials [1]. In the field of stem cell therapy research, there is a global pattern of "one super many strong". Compared with the United States, China's cell therapy research is not early, but the development speed is faster. In the field of cell therapy regulation, the United States has formed a mature and complete system.
Overview of the U.S. cell therapy regulatory system
In the United States, cell therapy is classified as biological products, and the Center for Biological Products Evaluation and Research (CBER) of the United States FDA is uniformly responsible for the approval and supervision. The cell therapy regulatory system consists of three parts: upper laws, regulations, management systems and guidelines, and the cell therapy is evaluated according to the size of the risk to develop different norms to adjust.
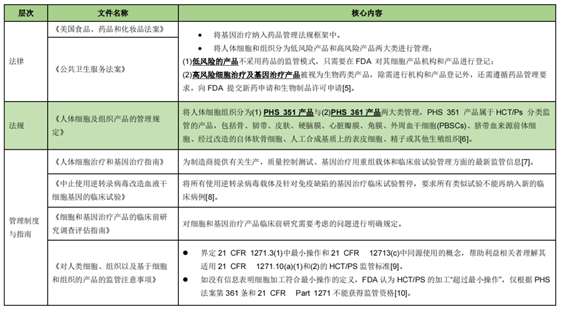
Key points of compliance supervision and compliance suggestions
Key points of foreign capital restriction compliance supervision and compliance suggestions
The United States has always regarded biotechnology and gene therapy as key areas of national technology. In terms of export and foreign investment access, a series of control measures have been taken to prevent the outflow of technology and maintain its international leading position in the field of biotechnology. The United States Department of Commerce (BIS) has export controls in the biotechnology sector in the Commerce Control List (" CCL "), which includes specific control categories including :1C351 human and animal pathogens, toxins; 1C353 Genetic elements and genetically modified organisms; 1C991 Vaccines, immunotoxins, medical products, etc. The United States Bureau of Industry and Safety in December 6, 2021 supplement: 1C991 "immunotoxin" refers to a monoclonal antibody that binds to a toxin and is intended to destroy a specific target cell without affecting neighboring cells [12], i.e., cell therapy.
The United States has different levels of export control for cell therapy, which is stipulated in The Foreign Investment Risk Review Modernization Act of 2018 (2018 Foreign Investment Risk Assessment Modernization Act, "FIRRMA"), The Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) will conduct a review of foreign investors mainly for the purpose of protecting national security, and the first consideration is "whether the country's investment is aimed at acquiring core technology", and the fifth is "whether it may expose citizen information, genetic information to foreign governments or foreign natural persons" [13]. Therefore, foreign investors who want to invest in the field of cell therapy, whether through mergers and acquisitions or investments, do not rule out facing the corresponding review of CFIUS.
Key points of cell therapy clinical research compliance supervision and compliance suggestions
The FDA classifies clinical research into investigational new drug (IND) and non-registered clinical trials (non-IND). Specific regulatory provisions are as follows:
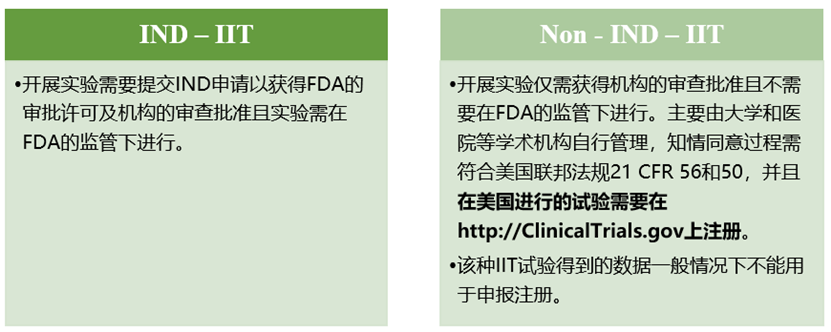
The United States divides IIT into three categories, of which: experimental drugs are managed in accordance with Non-IND-IIT research for use in post-market instructions, experimental drugs are managed in accordance with IND-IIT research for use outside the post-market instructions, and new drug research is managed in accordance with IND-IIT. In particular, experimental drugs for use outside the post-marketing marketing of research can be exempted from IND application under certain conditions, the exemption conditions are: (1) the test does not provide support for the application of new indications or provide a basis for major changes in the drug label; (2) The trial does not support significant changes in the advertising of prescription drugs; (3) The trial does not involve route of administration, dose, subject population, or other factors that significantly increase the risk of drug use; (4) The test operation complies with 21 CFR Parts 50 and 56 regarding institutional review boards and informed consent; (5) The trial was conducted in accordance with § 312.7 (Promotion and billing of investigational new drugs). Cell therapy companies need to pay attention to the corresponding research type and scope when carrying out the corresponding trial in the United States to carry out the corresponding IND declaration work.
Key points of cell therapy enterprise operation qualification compliance supervision and compliance suggestions
In the research and development process, in November 1976, FDA issued the draft regulations of GLP, which was formally implemented in 1979, requiring both project certification and laboratory certification to comply with GLP requirements [15].
In the registration process, the United States Quality Agreement Guide stipulates that MAH is ultimately responsible for the release of products to the market and the control of production or commissioning or the quality of materials [16]; In the manufacturing process, GMP in the United States is regulated by the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Administration Act (FDCA) and Part 200-299 of the United States Regulations of Federal Regulations. GMP certification procedures are divided into premarket inspection, routine supervision inspection and cause inspection. FDA will publish warning letters for serious violations in GMP inspection. For those who fail to reply in time or make adequate correction, sanctions such as stopping drug approval registration and issuing import ban shall be taken according to the risk [17].
Key points of regulatory compliance and suggestions on cross-border transfer of human genetic resources
The management of human genetic resources in the United States is mainly composed of the following institutions [19] :
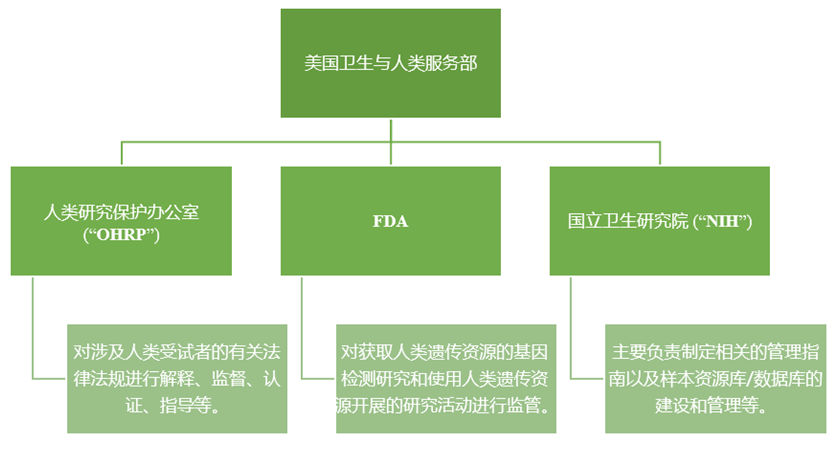
In 2003, 2007, and 2014, NIH issued and revised the Genome Data Sharing Policy (GDS), which requires all researchers who apply for project funding of more than $500,000 to NIH to submit a data sharing plan or data confidentiality statement, and share scientific data as required. In terms of the privacy protection of subjects involved in data sharing, the United States has also introduced relevant laws, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Liability Act (HIPAA), the Anti-Genetic Discrimination Act, etc., in which HIPPA clearly puts forward the standard of de-identification of protected health information; The Anti-genetic Discrimination law puts forward principles for the management and protection of human genetic resources such as the principle of informed consent and the maintenance of personal genetic confidentiality [20].
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Subject Protection Regulations and the Privacy rules in the Health Insurance Privacy and Accountability Act, human genome data submitted to the NIH-designated data repository must be de-identified and a confidentiality certificate of the database obtained as an additional precaution to prevent the mandatory disclosure of any personally identifiable information [21]. Otherwise face the appropriate punishment.
Key points of regulatory compliance and compliance suggestions for cell therapy companies in listing review
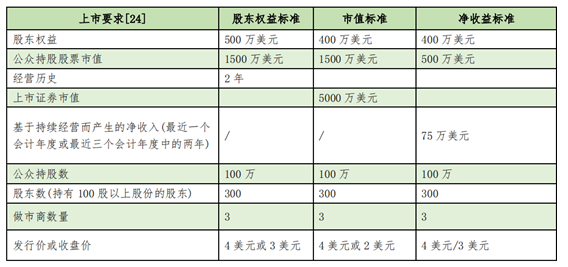
In the U.S. NASDAQ listing Standards, biomedical companies such as cell therapy are not required to have phase 1 or Phase 2 core products, but only set clear standards for market capitalization and net income.
- Discussion on the improvement of the US regulatory system and compliance issues
In summary, it can be found that the US regulatory system has two advantages: one is to classify and standardize the risk level of cell therapy to achieve accurate supervision; Second, the national regulatory bodies are clear, and the powers and responsibilities of each regulatory body are clear.
The relevant national regulatory system will become increasingly standardized, comprehensive and meticulous, for China's cell therapy enterprises and institutions, on the basis of research and development strength, improve the quality control of laboratories and clinical trials, comply with the registration/filing and GMP and GCP related requirements is also a part of cell therapy enterprises and institutions must do a good job.
