According to a statistic by Nature, the number of cell therapy R&D pipelines in China reached 695 in 2021, leading the global cell therapy R&D pipeline together with the United States [2]. In the field of cell therapy supervision, China's regulatory authorities have successively introduced cell therapy-related policies and systems, and have gradually built a unique regulatory system in the field of cell therapy in China.
Cell drugs represent products and enterprises in the classification of cell therapy
At present, cell therapy is divided into immune cell therapy and stem cell therapy. Among them, immune cell therapy is mainly divided into the following categories:
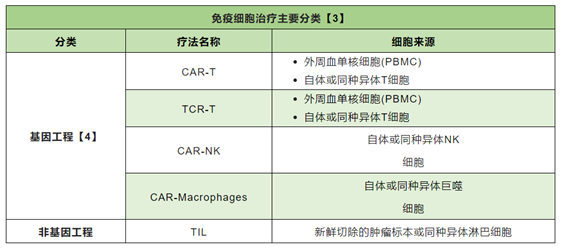
In recent years, research in the field of cell therapy in China has mainly focused on CAR-T cell therapy. It is worth noting that among the eight approved CAR-T therapies in the world, two products are from China, namely: Akilencel injection (Fosun Kat product), which was approved for market in June 2021, and Rechiolencel injection (Pharmajunol product), which was listed in September 2021. However, TCR-T therapy and stem cell drugs are currently in the early stage of development in China, and no products have been approved for market.
Overview of cell therapy regulations, overview of China's cell therapy regulatory system
After sorting out, China's cell therapy supervision can be divided into two paths: medical technology and drugs, and roughly through three stages, from 1993 to 2015, the supervision is relatively loose; In 2016, strict adjustment phase; The comprehensive specification stage from 2017 to now, the specific contents are as follows:
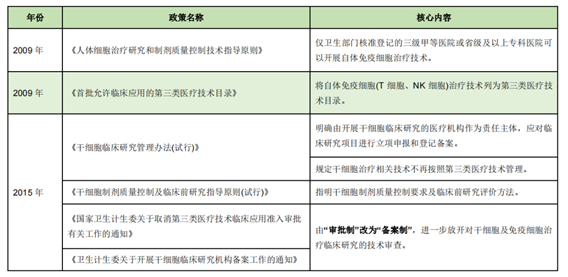
(1) The relatively relaxed stage from 1993 to 2015
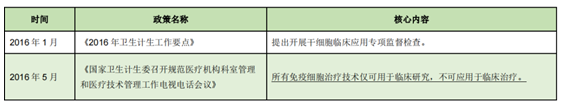
(2) In 2016, the stage of strict adjustment
Before 2016, China has recognized the broad prospects of cell therapy, and various policies mainly emphasize the importance of cell therapy, supervision is generally loose, cell therapy companies are in a state of free development, a large number of clinical research projects are carried out, and there are many cell therapy chaos, especially the "Wei Zexi" incident in April 2016. Reflecting the regulatory loopholes in cell therapy in China at that time, the state subsequently adjusted the corresponding regulatory scale.
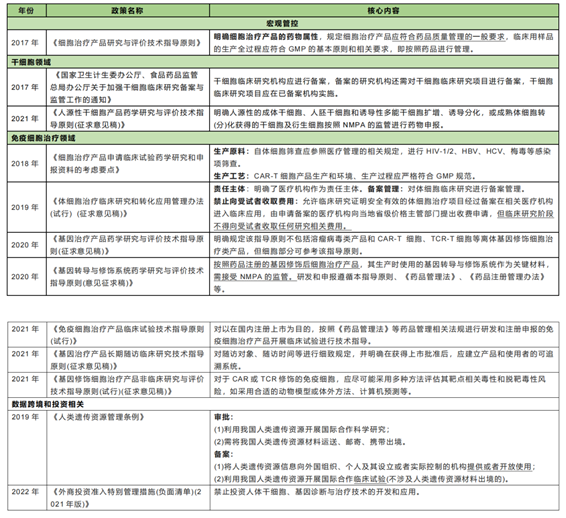
(3) After 2017, the comprehensive regulation stage
National ministries and local governments began to issue corresponding documents in 2017, vigorously promote the research and application of cell therapy technology, and standardize and guide the development of the entire cell therapy industry.
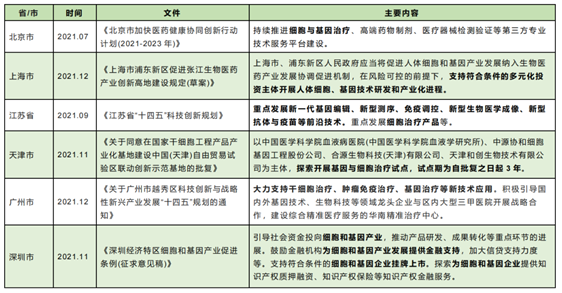
It is worth noting that since 2021, a number of Chinese provinces/municipalities have issued relevant documents (see the table below) to support the sound development of the cell therapy industry and promote international cooperation and introduction of cell therapy technology research and development, etc. It is foreseeable that the future foreign investment access conditions and development supervision in the field of cell therapy will show a relaxed trend.
Key points of compliance supervision and compliance suggestions
Key points of foreign capital restriction compliance supervision and compliance suggestions
China's "Catalogue of Industries to Encourage Foreign Investment (2020 edition)" lists the research and development and production of cell therapy drugs (except for areas where foreign investment is prohibited) as the catalogue of foreign investment encouragement. The development and application of human stem cells, genetic diagnosis and treatment technologies are listed as prohibited areas for foreign investment in the "Special Management Measures for Foreign Investment Access (Negative List)(2021 version)", which will be implemented on January 1, 2022. It is worth noting that according to the Technical Guidelines for Non-clinical Research and Evaluation of genetically Modified cell therapy Products (Trial)(draft for Comment) and the Technical Guidelines for Pharmaceutical Research and Evaluation of Immune Cell Therapy Products (Draft for Comment), CAR T cell therapy and TCR-T cell therapy belong to genetically modified immune cell therapy. Not stem cell therapy. Therefore, at present in our country, foreign investors can invest in immune cell therapy such as CAR-T therapy and TCR-therapy, but cannot directly invest in stem cell therapy.
In practice, according to Article 36 of the Foreign Investment Law and other relevant provisions, the company's equity held by foreign shareholders has the risk of being disposed of by the competent commercial authorities within a time limit [11]. In this case, the company will usually set up and adjust its internal architecture. Among them, the common arrangement is: the first step is to set up another domestic company as an entity such as cell therapy product research and development; In the second step, the relevant entity and the domestic company sign a series of control agreements (" control Agreement "or" VIE ") such as the Exclusive Business Cooperation Agreement, the Exclusive Purchase Right Agreement, the equity Pledge Agreement and the Power of Attorney; The third step is to complete the industrial and commercial registration of the equity pledge of the domestic company as an obligation within a certain period after the delivery of foreign investment. It should be noted that the feasibility, legitimacy and effectiveness of the aforementioned practice arrangement depends on the update requirements of future laws and regulations from time to time and the regulatory caliber of relevant government departments. Considering that the specific regulatory caliber in practice will be subject to the discretion of the specific regulatory authorities to a certain extent, on the basis of understanding the aforementioned risks, it is necessary to maintain communication with the relevant regulatory authorities to clarify the regulatory requirements and caliber that may be adjusted from time to time.
Key points of cell therapy clinical research compliance supervision and compliance suggestions
Clinical research/trials in China are mainly divided into two types. The Investigator-Initiated Clinical Trial is an investigator-initiated clinical trial with the primary purpose of improving clinical treatment. IIT and Industry-Sponsored Clinical trials (IST) by pharmaceutical companies. The former is to improve the clinical treatment level of listed drugs or to carry out medical research, etc. The latter is to prove the effectiveness and safety of new drugs to declare drug registration and listing. At present, China regulates IIT and IST through different legal regulatory systems:
If China adopts IIT clinical research, cell therapy enterprises should prevent illegal acts such as unauthorized charging and irrational use of funds. Otherwise, according to the provisions of Article 27 of the "Clinical Research Management Measures", health professionals and technicians will be dealt with accordingly; Medical institutions that fail to perform their supervisory duties will also bear corresponding administrative responsibilities; If the case constitutes a crime, it shall be transferred to the judicial organ for handling.
Key points of regulatory compliance and compliance suggestions for the operation qualification of Chinese cell therapy enterprises
For registration and commercialization of drugs, cell therapy companies need to meet the corresponding regulatory requirements of drugs in all aspects of research and development, registration, production, operation and use. According to the provisions of China's Drug Administration Law:
In the research and development process, enterprises should comply with the "Non-clinical Drug research Quality Control Code" (GLP), "Drug Clinical Trial Quality Control Code" (GCP), to ensure that the whole process of research and development in accordance with the law; In the registration process, MAH system shall be implemented, MAH shall establish a drug quality assurance system, equipped with specialized personnel independently responsible for drug quality control, MAH may entrust other enterprises to produce by signing the entrustment agreement and the quality agreement, but shall not entrust the obligations and responsibilities legally performed by MAH to the trustee through the quality agreement;
In the production process, the enterprise should meet the requirements of the GMP on the enterprise personnel, plant facilities, production environment, production management, quality control and other links, establish the enterprise drug quality control system, and meet the drug GMP conditions of the drug regulatory department;
In the business link, whether wholesale or retail, the enterprise should follow the "Quality Control Code for Drug Distribution" (GSP) and meet the GSP requirements within the time specified by the drug regulatory department.
In practice, there are not a few enterprises in violation of GMP and GSP. At the end of 2020, Liaoning Food and Drug Administration, Guangxi Food and Drug Administration and Tianjin Municipal Regulatory Commission announced a penalty notice for 5 pharmaceutical enterprises in violation of GMP, and the penalty result was a warning or suspension of production; In December 2020, the Hunan Provincial Drug Administration publicized the "Hunan Province Drug Circulation Flight Inspection and Treatment Notice", in the flight inspection of 30 operating enterprises, a total of 24 were ordered to rectify within a time limit, 6 enterprises seriously violated the requirements of drug GSP, were punished by cancellations of the "drug distribution license", suspension of operations and other penalties. Therefore, cell therapy enterprises should pay attention to the corresponding requirements of GMP and GSP in the production and operation process to reduce the risk of administrative punishment.
In addition, for the research of stem cells, immune cell therapy institutions and enterprises, should comply with the "Stem cell clinical research Management Measures (trial)" and refer to the "Somatic Cell Therapy Clinical research and transformation application Management Measures (trial)(draft for comment)" qualification provisions.

Key points of regulatory compliance and suggestions on cross-border transfer of human genetic resources in China
The cross-border transfer of human genetic resources in China is based on the Regulations on the Management of Human Genetic Resources (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations) promulgated by The State Council in 2019 and the Biosafety Law promulgated by the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress in 2020. These two documents clearly prohibit and restrict the use, carrying and protection of human genetic resources in China. Since China's laws on the regulation of human genetic resources involve collection, preservation, utilization, external provision (transmission) and other links, and cell therapy companies inevitably involve regulatory requirements in the development and operation process, therefore, the existence of corresponding regulatory risks cannot be ruled out. In particular, the Regulations stipulate that overseas organizations, individuals and institutions established or actually controlled by them (foreign units) shall not collect or preserve Chinese human genetic resources within the territory of China, and shall not provide Chinese human genetic resources overseas. The details are as follows:

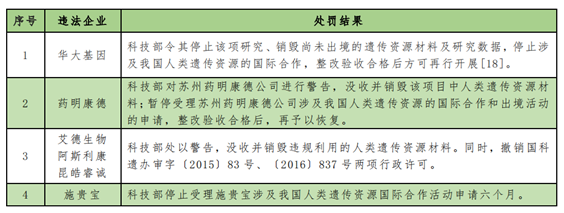
In addition, we have also paid attention to some cases of administrative penalties in regulatory practices: for example, the Ministry of Science and Technology announced the information of administrative penalties on human genetic resources on October 24, 2018, and a total of six enterprises including BGI and Kangde were punished, and the illegal facts include:

Another example is that Bristol-Myers Squibb (China) Investment Co., LTD. (hereinafter referred to as Squibb), as the sponsor, entrusted Enkang Clinical Medical Research (Beijing) Co., LTD. (hereinafter referred to as Enkang) to apply for the administrative license for international cooperation activities on human genetic resources in China, and relevant business personnel of Enkang forged the official seal and legal person signature and submitted false application materials to the regulatory authority. The Ministry of Science and Technology announced on December 20, 2020 that it had made a decision to punish those who had obtained administrative licenses for human genetic resources collection (international cooperation) activities in violation of relevant regulations.
If the daily business of cell therapy enterprises involves the cross-border of human genetic resources in China, when transporting, mailing, and carrying out outbound human genetic resources materials in China, it should be declared and reviewed by the relevant departments of the Ministry of Science and Technology. Otherwise, according to the provisions of Article 38 of the Regulations, they will face corresponding penalties by the Customs in accordance with laws and administrative regulations.
Key points of regulatory compliance and compliance suggestions for Chinese cell therapy companies in listing review
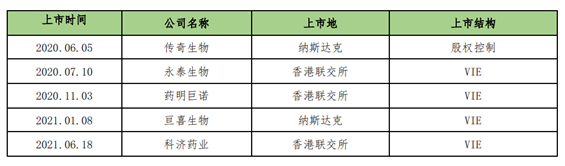
As of August 31, 2021, a total of five CAR T cell therapy companies in China are listed overseas (including Hong Kong), and the basic information and listing structure of their listing are as follows:
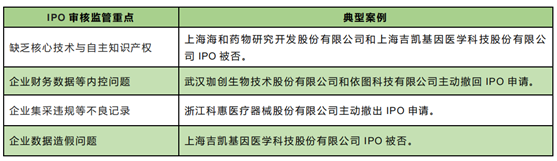
At present, there are no cell therapy companies listed in the domestic market, in order to give enterprises compliance recommendations, the following is a summary of the core review requirements of biomedical companies in the science and technology board. According to the Rules for the Listing of Stocks on the Science and Technology Board of the Shanghai Stock Exchange (the "Science and Technology Board Listing Rules"), at least one core product of a biomedical company applying for the fifth set of listing standards is allowed to carry out phase 2 clinical trials [22]. In the year 2021 (as of December 29, 2021), a total of 17 biopharmaceutical companies have terminated their ipos on the science and technology board. After reviewing the specific reasons for their termination, it can be understood that the focus of listing review and supervision mainly includes the following four aspects:
Therefore, for cell therapy enterprises with the goal of listing in China, they should pay attention to their independent research and development of core technology products and integrity and compliance operations, and ensure the authenticity of various corporate data.
Discussion on the improvement of regulatory system and compliance
China's cell therapy regulatory system has problems such as indistinct differentiation, "one-size-fits-all", unclear regulatory bodies and corresponding responsibilities, which restricts the further standardized development of China's cell therapy industry. The regulatory bodies of different stages and products of cell therapy should be clearly defined, and different regulatory rules should be formulated for stem cell and immune cell therapy according to the product risk level. For low-risk cell therapies, medical technology filings can be used to simplify approval procedures and speed up clinical research or trials. For high-risk cell therapies, clinical study design can be strictly regulated through review and approval procedures to avoid trial risks. The relevant national regulatory system will become increasingly standardized, comprehensive and meticulous, for China's cell therapy enterprises and institutions, on the basis of research and development strength, improve the quality control of laboratories and clinical trials, comply with the registration/filing and GMP and GCP related requirements is also a part of cell therapy enterprises and institutions must do a good job.
