summarize
At present, China's cell industry is diversified in real forms, and there is a large space for clinical research, research and development, production capacity and market demand in the cell field. On the other hand, from the main regulatory authorities to local governments around the country, or carefully handle in specific regulatory cases, reserve sufficient policy space for improving the regulatory blank in the future, or actively explore the development model and regulatory path of the cell industry.
This paper intends to sort out the actual formats of the cell field spawned by the market-oriented mechanism (rather than from the perspective of the industrial chain), as well as judicial and regulatory practice cases in various regions, and analyze and judge the future development model and regulatory path of China's cell industry based on the underlying logic and relying on the elements of regulation, so as to provide reference for the industry. Unless expressly stated as "stem cell" or "immune cell", the term "cell" herein includes somatic cells, immune cells, stem cells, etc.
First, the current format and typical construction mode of China's cell industry
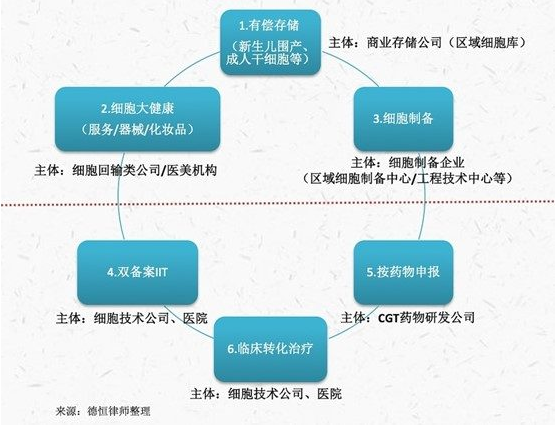
1. Current status of commercial cell storage
At present, China's cell storage business is divided into public blood bank hematopoietic stem cell storage and commercial paid storage, the tissue samples involved mainly include newborn umbilical cord, umbilical cord blood and placenta samples, bone marrow fluid samples, tooth samples, adipose tissue, synovial tissue and so on.
The public bank mainly consists of 7 cord blood hematopoietic stem cell banks in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Shandong, Guangdong and Sichuan successively approved by the former Ministry of Health to collect and store cord blood hematopoietic stem cell banks for the purpose of public welfare in accordance with the regulations of the Regulation on the Setting and Management of Cord Blood hematopoietic stem cell Banks (Trial) and other regulations for the use of patients in need.
Commercial storage by relevant enterprises for the public engaged in paid cell storage and preparation, mainly neonatal autologous perinatal tissue stem cells and adult autologous cells. At present, all provinces have paid cell storage business, and it shows the siphon effect of the head enterprise. For example, Zhongyuan Union (600645) disclosed in its 2022 annual report that it has established a cell resource bank in 20 provinces and cities across the country, and carried out the detection, preparation and storage services of cord blood hematopoietic stem cells, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, placental subtotipotent stem cells, fat stem cells and immune cells, and built a national cell resource storage network.
2. Cell production and preparation status
In addition to cell drug research and development and preparation enterprises and related CDMO enterprises, the current cell preparation business mainly refers to cell enterprises to provide cell products for clinical research hospitals, scientific research and enterprises and institutions. As disclosed in the annual report of Tianqing Shares (832035), the company's preparation service projects are "mainly concentrated in professional cancer hospitals and general hospitals in the province and the three eastern provinces, oncology, general surgery and other departments that produce tumor patients, and the company provides efficient NK cells for their biological therapy cancer clinical research." By the end of 2022, the number of China's stem cell quality inspection reporting institutions has been about 50. In recent years, with the continuous maturity and expansion of induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) technology and its application, the market demand for the preparation of IPSC-derived seed cells and precursor cell preparations continues to expand.
In the context of local governments encouraging the development of cell and gene therapy, head cell enterprises are mostly identified by local science and technology, development and reform departments as local "engineering technology center", "engineering research center", "regional cell preparation center" and so on. As Celera (831049) has disclosed in the letter file, Guangdong Province (Celera) regional cell preparation center is the Guangdong Development and Reform Commission, the provincial Science and Technology Department, the provincial Health and Family Planning Commission, and the provincial Food and Drug Administration jointly issued a letter of approval, and the provincial regional cell preparation center undertaken by Celera.
3. Current status of cell medical Beauty and Great Health business
Cell health business common stem cells, immune cell transfusion and related medical products or services. For example, Guanhao Biology (300238) disclosed in the 2021 annual report that the company "rooted in the forefront of health, timely launch of immune enhancement programs, dental pulp stem cell storage and other new technical services, with the expansion and upgrading of product lines, self-built traditional Chinese medicine health care center - Tianyou Yannian Hall, high-end comprehensive clinic - Guangzhou Bainifu and other technical operation institutions, Improve the closed loop of product application."
It is worth mentioning that because human cell factor has not been included in the list of cosmetic apis of the State Food and Drug Administration, there are no approved stem cell cosmetics in China. The State Food and Drug Administration issued a document in September 2021 emphasizing that "stem cell cosmetics" are pseudo-concepts. At present, the cosmetics produced and sold in compliance are not cosmetics based on "human cells" as raw materials. For example, Celera has disclosed that "relying on the core stem cell technology mastered by the company, the company extends to the research and development of animal and plant cell extract technology, and converts the animal and plant cell extract raw materials that are independently developed and independently produced including patented technology into functional skin care products."
4. Declare by drug
With the approval of two CAR-T products in China in 2021, cell therapy products are fully opened up in accordance with the path of drug supervision. According to the CDE official website information, as of February 28, 2023, a total of 62 stem cell drug clinical trial applications (IND) of 42 domestic companies were accepted, and 47 of 30 companies were clinically implied licenses, mainly from umbilical cord, placenta, bone marrow, fat, dental pulp, uterine blood and other mesenchymal stem cell drugs. At the same time, IND applications for IPSC stem cell drugs are also gradually increasing. At present, the more active enterprises in this area include Anhui Zhongsheng Traceability, Nanjing Elpu, Zhejiang Hode Biological, Chengnuo Medical, Wuhan Ruijian Pharmaceutical and so on.
It is worth mentioning that in April this year, Sibiman Biotechnology officially announced the launch of the Phase III clinical trial of the company's "AlloJoin human adipose mesenchymal progenitor cell injection". This also marks China's stem cell drug research and development into the phase III clinical era.
5. Current status of double-filed clinical trials
Double filing means double filing of research institutions and research projects for non-registered clinical research (IIT).
After searching, 137 research institutions (including 22 military hospitals) in the country have completed the record of clinical research institutions in the Health Commission, the Food and Drug Administration or the Health Bureau of the Ministry of Logistics Support, a total of 112 stem cell clinical research projects for the record. Relevant indications involve the treatment of circulatory system (such as acute myocardial infarction, heart failure), nervous system (such as Parkinson's disease, ischemic stroke), urogenital system (such as cervical adhesion, premature ovarian failure), immune system (such as lupus nephritis), motor system (such as knee osteoarthritis, meniscus injury, etc.) and other multi-system diseases.
6. Current status of clinical conversion therapy
Despite changes in regulatory policies, in medical practice, hospitals or companies have never stopped trying or implementing cell clinical transformation therapies in a variety of ways. Many local governments or free trade zones are also actively exploring, hoping to open up the payment path of cell clinical transformation therapy. As disclosed in the 2021 annual report, "In June 2021, the Blood Research Institute cooperated with the company and other subjects to build the China (Tianjin) Pilot Free Trade Zone linkage innovation demonstration base, which plans to rely on the national stem cell engineering product industrialization base cell storage, research and development, production and preparation, clinical transformation application and other closed-loop management environment." To explore breakthroughs in compassionate drug use in cell therapy clinical trials, the import of foreign and domestic unlisted drugs and medical devices, and the clinical charging application of cell therapy in accordance with medical technology access."
(2) The current typical investment and construction mode of cell enterprises
In view of the long research and development cycle of cell therapy drugs and the characteristics of capital intensive, most domestic cell enterprises at the same time layout a variety of business formats to build a full closed-loop cell industry. Taking domestic listed or listed cell enterprises as an example, their business layout is as follows:

For another example, according to public market information, Beijing Hanshi United Biotechnology Co., Ltd. also has four industrial segments: Hanshi Biological, Hanshi Pharmaceutical, Hanshi Medical and Sino Shenzhou, among which Hanshi Biological is responsible for cell storage, preparation and CXO service; Han's Medical undertakes the construction and operation tasks of the Group's precision medical health industry, which mainly includes tertiary hospitals, comprehensive outpatient departments, high-end physical examination centers, third-party medical inspection centers, Internet hospitals, medical beauty care centers, medical tourism and other businesses. Han's Medicine is mainly focused on the research and development of cell new drugs, and a number of clinical trials of stem cell class 1 new drugs have been approved.
Second, the legal evaluation and judicial supervision practice of existing business forms
(I) The overall characteristics of the current judicial supervision practice
At present, the judicial adjudication in the field of cell in our country is mainly sporadic cases, and no systematic adjudication standard has been formed. The practice of administrative supervision is mainly passive supervision initiated by complaints and reports of relevant subjects, and the active research and judgment type and systematic supervision are relatively less.
It is worth mentioning that in order to cope with the regulatory challenges brought by the development of the industry, some places have begun to strengthen the research of active regulation. For example, in September 2021, Shenzhen Pingshan District People's Court issued the bidding announcement on the special research topic of "Research on Legal Risks and Judicial Responses of the Whole Process of the Biomedical Industry", and in December 2022, Shenzhen Pingshan District issued the "Guidelines on Criminal Compliance Work of Biomedical Enterprises in Shenzhen Pingshan District", which are all initiatives to build local adjudication or supervision systems.
(2) Typical judicial and regulatory cases of each business type and their execution caliber
1. Legal evaluation and judgment of commercial storage business
(1) Validity of commercial storage contracts
Taizhou Intermediate Court (2017) Su 12 Min End 570 case, the court defined the cord blood storage dispute as a consumer rights dispute; In terms of the validity of the contract, the court held that the appellant "is both the provider and owner of umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells, and the umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells can only be used by himself or his close relatives," in response to the claim that "the contract involved in this case violates the mandatory provisions of laws and administrative regulations and should be invalid." It does not involve other citizens, nor will it affect public safety ", therefore, "the appellee's acceptance of the preparation and storage of umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells entrusted by the appellant does not violate the mandatory provisions of laws and administrative regulations such as the Blood Donation Law of the People's Republic of China", and the final judgment is that the paid storage contract of umbilical cord blood is valid.
After searching in the website of judgment documents, the author has not found the case cases of commercial storage disputes after the promulgation of the personal relics regulation.
(2) Regulatory practices for commercial storage and depository approval
Most of the current enterprises engaged in commercial cell storage have positioned the storage behavior as based on "future clinical treatment purposes" and have not applied for storage permission. Some enterprises have applied for and obtained preservation approval because of both future scientific research purposes or specific platform functions, such as Henan Province Hualong Biotechnology Co., LTD. Henan Human stem cell resource Bank.
There have been no cases of commercial storage companies being punished by the regulatory authorities for failing to obtain a preservation permit.
2. Judicial practice of the validity of cell transfusion protocol
In the existing dispute cases related to cell transfusion, there are two different judgment results, "valid" and "invalid", regarding the validity of cell transfusion protocol.
(1) Cases where the agreement is valid
In the Yantai Intermediate People's Court (2020) Lu 06 Minend 1331 case, the above-mentioned person (the recipient of the return transfusion) proposed that "the appellee directly injected the 'stem cell transfusion' into the Appellant without the approval of the State and charged the Appellant a fee. In violation of the above administrative measures and the provisions of the Drug Administration Law of the People's Republic of China, the Regulations on the Administration of Medical Institutions and other laws, the "stem cell package" service provided by the appellee for payment to the Appellant in the name of "immune cell health care" shall be deemed invalid according to law. The court of second instance finally held that "the 'stem cell package' service contract signed by the two parties in this case was a genuine expression of the intentions of the two parties, and the contract did not violate the mandatory provisions of laws or administrative regulations when the two parties signed the contract", that is, the cell health care contract was valid.
(2) Cases in which the agreement is invalid
In the Shanghai No. 1 Intermediate People's Court (2020) Hu01 Mindu 4321 case, the court held that "the management norms related to stem cells have the attribute of public interest, although the" Management Measures for Stem Cell Clinical Research (Trial) "does not belong to laws and administrative regulations, but belongs to departmental regulations at the level of effectiveness of legal norms. However, the management measures are formulated in accordance with the "Drug Administration Law of the People's Republic of China" and "Regulations on the Administration of Medical Institutions" and other laws and administrative regulations, aiming to regulate and promote the healthy and orderly development of stem cell clinical research. "Therefore," Juren Company sells' stem cells' to others for direct human transfusion, Violation of the "Stem cell Clinical Research Management Measures (Trial)" article 52 on the prohibition of stem cells directly into clinical application at the same time, a serious violation of ethical norms, destroy the national medical supervision system, endanger the life and health safety of unspecified individuals, and then damage the social public interests, the final judgment agreement invalid.
To sum up, there is no uniform standard in judicial practice for the legal evaluation of cell medical beauty and cell health services.
3. Regulatory practices of "cellular cosmetics"
The Advertising Supervision Department of the State Administration for Market Regulation, "Tips on Strengthening the supervision of stem cell advertising" (Guanghazi (2021) No. 187), and the State Food and Drug Administration, "Notice on carrying out special actions on cosmetics" Online net and offline clean source "(the State Food and Drug Administration makeup (2021) No. 47) and other documents are clearly prohibited from illegally claiming that related products contain stem cells and exist Beauty, anti-aging and other effects, many places also appear administrative punishment cases.
Therefore, the regulatory caliber of "cell cosmetics" is relatively clear.
4. Judicial supervision of clinical conversion therapy
For a long time, there have been few criminal cases involved in clinical conversion treatment in China, and the more representative one is the illegal business crimes of Xu and others at No. 76 of Xingchu in Shanghai 0101 (2020). The judgment of the case states that between December 2016 and April 2017, Xu recruited patients in the name of the Translational Medicine Research Institute of a university in Shanghai, and Wang was responsible for producing stem cell injection at the office of the company involved in the case, and finally injected stem cells at the oncology department of the hospital involved or the company's office for patients suffering from different diseases such as ALS disease and cerebral hemorrhage.
The trial was fascinating. Initially, the Shanghai Huangpu District Court of first instance decided that Xu Mou and others committed the crime of producing and selling fake drugs, and the public prosecution organs and the defendants of the original trial were not satisfied, respectively, and filed a protest and appeal. Shanghai Third Intermediate People's Court on the grounds that "whether the stem cells involved in the case are counterfeit drugs and the status and role of each defendant in the joint crime need to be further ascertained", ruled to remanded for retrial. In January 2020, the Huangpu District Court filed a retrial, and the Huangpu District Procuratorate changed the charges to illegal business crimes. In the end, the Huangpu District Court ruled that the defendant Xu Mou "violated the national drug monopoly and monopoly management laws and regulations, operating drugs without permission", constituting the crime of illegal business. Xu's sentence was changed from 11 years in prison for producing and selling fake drugs to six years in prison for illegal business.
At the same time, for cell clinical transformation therapy, typical administrative punishment cases in the past two years are as follows:
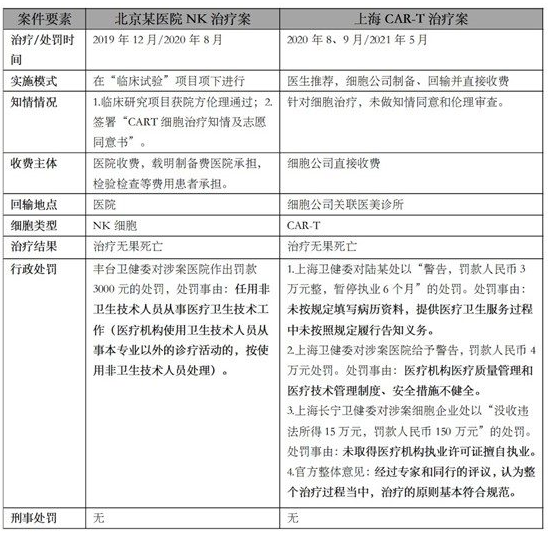
Up to now, the parties involved in the above cases have not been involved in criminal punishment.
5. Other judicial practices related to the field of cells
At present, the criminal charges related to the cell industry mainly include the crime of selling fake drugs, fraud, smuggling, obstruction of inspection and quarantine and other import and export crimes, among which the fraud case is the first, which is also related to the popularity of cell therapy knowledge in China and the supervision blank. Typical cases in recent years are as follows:
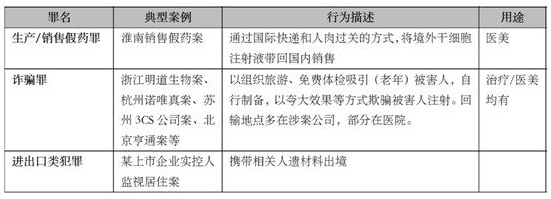
In summary, although there are only a small number of judicial decisions and regulatory punishment cases, it can also be seen that the relevant courts and regulatory departments are cautious and restrained in reserving policy space for the development of the industry when dealing with specific cases, and there also seems to be a trend of leniency in judicial decisions.
Third, China's cell industry supervision trend research and analysis
(1) The basis for research and analysis
1. Common underlying logic or maximum common divisor based on foreign regulatory models
We believe that whether it is the US "monorail" (similar to the European Union) that constructs a regulatory system based on the Public Health Service ACT that divides human cells and tissues into low-risk products (PHS ACT Section 351) and high-risk products (PHS Act Section 361), Or the Japanese "dual-track system" of parallel legislation of regenerative cell therapy products and drugs and medical devices, all of which have common underlying logic and element support. Mainly reflected in the following two points:
(1) Relying on a sound risk classification system
According to the risk level of cell and tissue products, the FDA classifies products into the following two categories, and clearly defines the meaning of "minimal operation" and "homologous use" :
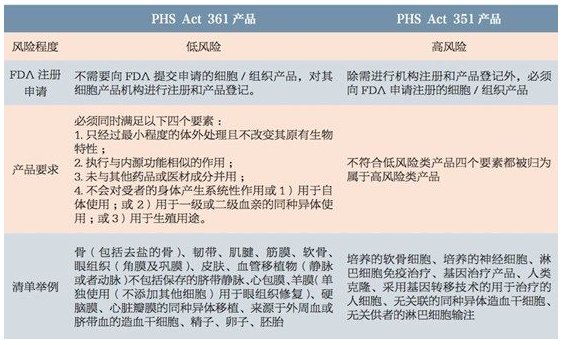
Source: China Food and Drug Administration
Japan by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) in accordance with the three levels of risk for cell therapy to declare the record management, as follows:
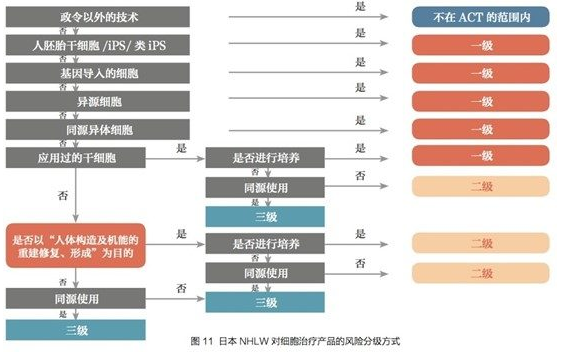
Source: China Food and Drug Administration
(2) Relying on a complete cell preparation system and market
For cell preparation systems, the US FDA has developed relatively complete guidelines, including process-related guidelines, pre-clinical guidelines, guidelines for specific diseases or specific cells, effectiveness and safety guidelines. The Japanese Cell Therapy Guide also covers different disease areas and cell types, focusing on cell collection, cell preparation, quality evaluation, efficacy safety evaluation, and transportation and storage standards, basically achieving the standardization of cell preparation.
Regarding the cell preparation and circulation market, taking stem cells as an example, according to market disclosure information, Japan has issued more than 2,700 cell preparation licenses by the end of 2020.
2. Based on the evolution logic of China's cell industry regulatory model
The future regulatory model is the extension and improvement of the past and current status quo.
China has implemented a "dual-track system" for a period of time, after the 2016 "Wei Zexi incident", the former National Health and Family Planning Commission terminated cell therapy charges, and the drug regulatory department gradually strengthened, clarified and improved the path and system of drug supervision. According to the current laws, regulations and normative system, the "positive list" in the field of cell gene therapy in China is as follows:
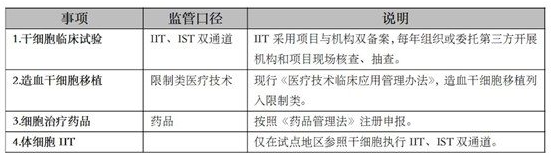
Regulation of areas outside the "positive list" is temporarily left blank, but trend logic is reflected in the relevant representation. For example, in 2019, the National Health Commission issued the "Regulations on the Clinical Application of New Biomedical Technologies (Draft for Comment)" and the "Management Measures for Clinical Research and Application of Somatic Cell Therapy (Trial)" (draft for comment), although it has not yet been promulgated, it is considered by the industry to be a signal of the return of the "dual-track system". On May 9, 2023, the National Health and Health Commission issued the Guidelines for Somatic Cell Clinical Research (Draft for Comment), which further reflects the trend of gradual convergence of somatic cell IIT and stem cell IIT regulatory models.
3. Based on the policy trend and legislative logic of China's cell field
In terms of policy, following the inclusion of the 13th Five-Year Plan, the 14th Five-Year Plan, and Healthy China 2030, at the beginning of 2022, nine departments such as the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Science and Technology, and the Health Commission jointly issued the "14th Five-Year Plan for the development of pharmaceutical Industry", proposing to focus on the development of cell therapy and other new biological drug industrialization preparation technology. In May 2022, the National Development and Reform Commission issued the "14th Five-Year Plan" for Bioeconomy Development, proposing the development of new technologies such as gene diagnosis and treatment, stem cell therapy, and immune cell therapy, accelerating the transformation and clinical application of related technological products, promoting the formation of new models of regenerative medicine and precision medicine treatment, and promoting policy first trials.
In terms of legislation, China has made intensive legislation or amendments in the fields of scientific and technological progress, biosecurity, human heritage resource management, data security, scientific ethics, foreign investment, technology import and export, etc., to build a legal system that is more in line with the current economic and technological development situation at home and abroad.
We believe that the basic logic of China's policy and legislation for the biotechnology industry such as cell therapy as a whole is "encourage development and hold the red line", as follows:
(2) Analysis of regulatory trends and the Chinese version of the "dual-track system"
1. Analysis of regulatory trends of commercial storage
In our view, it is unlikely that commercial storage self-repositories will be included in depository approval regulation for some time. For the "storage" behavior, the supervision will still be differentiated according to the "storage purpose", that is, only the sample database based on scientific research purposes requires storage qualification, as shown in the figure below:
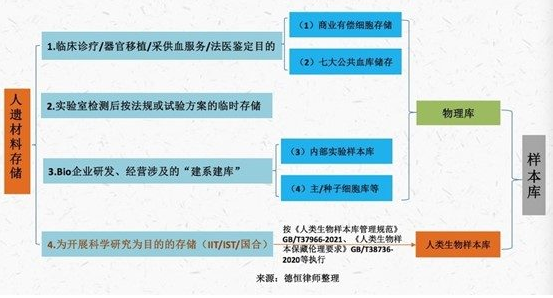
In particular, regardless of whether the storage permit has been obtained, enterprises and institutions engaged in stem cell storage should comply with the provisions of the Biosafety Law, the Regulations on human heritage, the Criminal Law and other laws and regulations on the supervision of human heritage resources, international cooperation, and the provision of human heritage information to the outside world without discrimination.
2. Analysis of regulatory trends of cell medical beauty and general health
On the one hand, some local governments support stem cell medicine as a local characteristic economy. For example, in the "Kunming Cell Industry Development Plan (2021-2035)" released by Kunming City in August 2022, it is proposed in the "recent key promotion" part that "clinical technology (disease treatment, medical beauty application) is the breakthrough point of the industry, open the clinical application link and payment link, and realize the breakthrough of clinical technology in multiple diseases"; In the "key tasks" part, it is clear that "actively develop stem cell beauty products, and introduce a number of medical beauty manufacturing enterprises with core technologies; Promote the construction of plastic surgery and cosmetology departments in medical institutions in Kunming, promote multi-direction research such as stem cell research and development, and the therapeutic application in repair and reconstruction, tissue regeneration, and wound repair; Give full play to the flow advantage of Kunming tourist resort, and develop tourism products with stem cell medical beauty service as the theme."
On the other hand, in the "Catalog of Used Cosmetic raw materials" revised and released by the State Food and Drug Administration in 2021, "stem cells" are not included as cosmetic raw materials. In the current clinical research on stem cells in China, there are few studies on the beauty and anti-aging of stem cells.
We believe that in the long run, the application of cell technology in the field of medical beauty and general health will be included in low-risk clinical transformed cell projects or pipeline regulation of health products and cosmetics, respectively. However, due to the relative lag of China's cell preparation system and market, the "double filing" threshold of stem cell clinical research is higher, the "stem cell products" are included in the raw materials of cosmetics and health products, or the "double filing" threshold is adjusted in accordance with the risk classification principle, and it is unlikely to land in the short term, therefore, the probability of the field is still in the regulatory blank for a period of time in the future. However, relevant exploration will not stop, for example, in January 2021, the "Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery" published "Expert consensus on research and clinical trials of stem cells in the field of plastic repair and beauty", aiming to provide reference and support for the research and future clinical transformation of stem cells in the field of plastic repair and beauty.
3. Analysis of the Chinese version of the "dual-track" model of cell therapy
Different local governments have different attitudes on whether to support the clinical translational application of cell therapy. Representative local policies include:
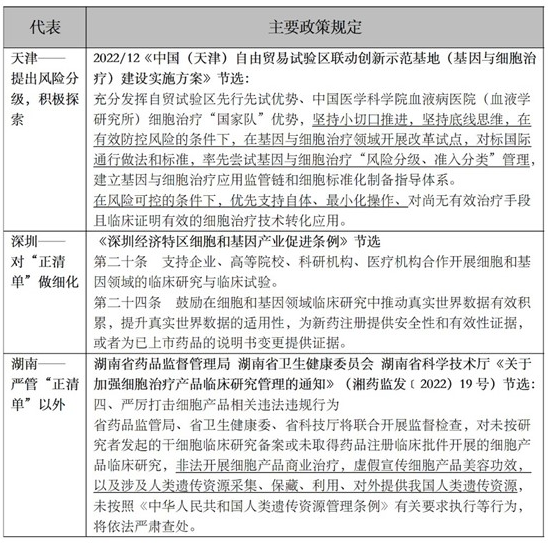
In view of the fact that most of the current record hospitals do not have the capacity of cell preparation, and the maturity of cell preparation technology and market capacity in China cannot meet the needs of fully liberalizing the clinical transformation of IIT projects, it is not possible to completely classify supervision according to the nature of the implementation subject; At the same time, if the regulation is only based on risk classification, it will close the clinical conversion pathway of most existing "double filing" projects, which will greatly reduce the value of existing IIT research and limit the feasibility. The advantages and disadvantages of the two modes are as follows:
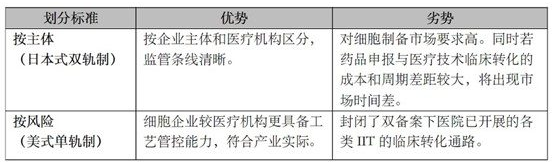
Correspondingly, China's cell industry research and development, production capacity and market demand capacity urgently need to be released.
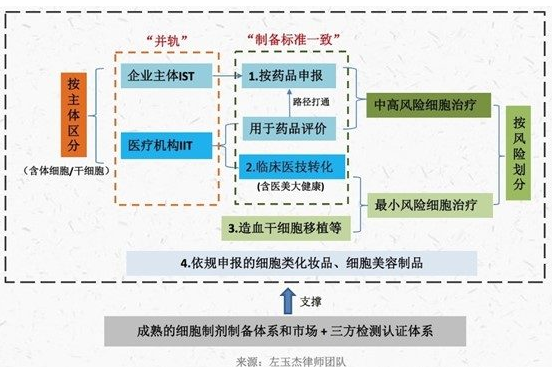
In summary, we believe that the supervision of cell therapy in China will have the following changes or trends (all contents or synchronous advancement) :
(1) The supervision of somatic cell and stem cell clinical research is gradually converging, that is, the implementation of "double filing";
(2) Take the lead in carrying out risk classification management in the "double filing" project, and try to liberalize the clinical transformation application and fees of low-risk projects;
(3) Improve the cell preparation system by type and disease, unify or converge the preparation standards of the same type of cells in different regulatory channels, and expand the cell preparation market and third-party inspection and testing market;
(4) Strengthen the integration of IIT and IST management, improve and optimize the path and mechanism of IIT data for new drug registration application, and further open up the "double filing" project results transformation channel;
(5) Use the regional innovation pilot mechanism to select more successful regions to expand the pilot.
The details are as follows
peroration
Although there is some uncertainty in the regulation of China's cell industry, we can still capture more certainty based on the underlying logic and factor analysis that affect the choice of regulatory model. For different organizations or institutions, it is appropriate to plan and respond in advance. For example, institutions engaged in cell medical beauty actively promote the IIT research and transformation of cells in beauty and anti-aging, and gradually incorporate cell medical beauty health projects into the business scope of medical institutions at all levels and all types, or its compliance development trend. For local governments, actively carry out active management layout, or improve the local business regulatory environment, and promote the development of the local cell industry.
reference
[1] Yantai Intermediate People's Court of Shandong Province (2020) Lu 06 Min End 1331 Civil Judgment;
[2] Shanghai No. 1 Intermediate People's Court (2020) No. 4321, Shanghai 01 Min End;
[3] Taizhou Intermediate People's Court of Jiangsu Province (2017) Su 12 Min End 570 Civil Judgment;
[4] Annotated Criminal Law, Chen Xing, 2022 edition;
[5] Progress and Prospect of Cell and gene therapy product regulatory Science, Gao Jianchao, Wei Wei, Zhang Min, Gao Chenyan, Center for Drug Evaluation, National Medical Products Administration, China Journal of New Drugs, volume 31, 2022
[6] Comparison of International Regulation of Cell and gene therapy Products and its implications for China, Yu Ganjun et al., China Food and Drug Regulation, 08, 2019;
[7] Annual Report of Guanhao Biotechnology Co., LTD., 2021 and 2022;
[8] Annual Report of Zhongyuan Union Cell Genetic Engineering Co., LTD. 2021 and 2022;
[9] Annual Report of Guangzhou Celera Stem Cell Technology Co., LTD., 2021 and 2022;
[10] Research on the Core Legal Mechanism and Problems of Induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) Technology, Transformation and Application, Lawyer De Heng, Zuo Yujie et al
